Services of Indian Police according to their ranks
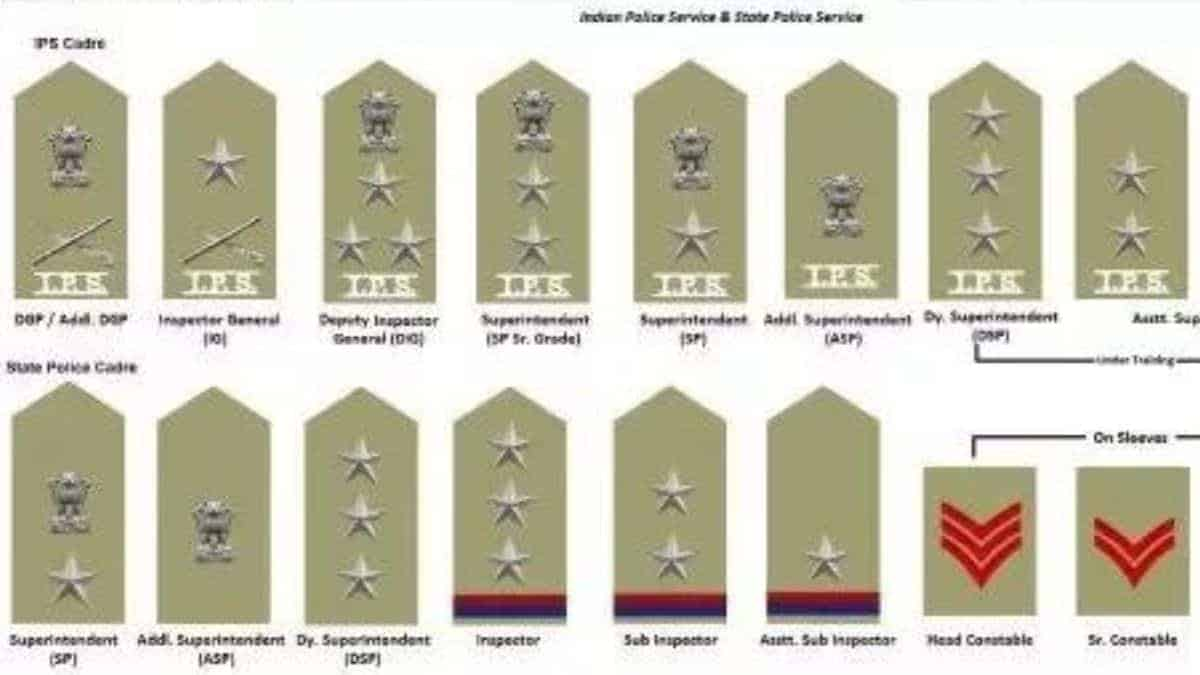
The Indian police service was established in 1905 as an Imperial police force around 117 years ago. After India got its independence in 1947, The Imperial Police Service got replaced by The Indian police service (IPS) in 1948. IPS is considered as a central civil service under All India Services.
According to the reports of 2016, the strength of the cadre is 3,894. Along with the Indian Administrative Service (IAS) and the Indian Forest Service (IFS). The IPS comes under All India Services and the officers are employed by the Union Government and by the individual states.
The Law force in the country is a state concern and hence, the structure of police varies from state to state. Each state has its own way of fixing its policing structure. But still there are ground rules and structure which can be observed.
The controlling authority of IPS (India police service) is the Ministry of Home Affairs. MHA is the overall incharge of internal and external security and policing.
The administrative head of MHA (Home Secretary) is an IAS officer in the rank of Secretary to Government of India.
The ministry has jurisdiction over the Seven Central Armed Police Forces which includes BSF (Border Security Force), CRPF (Central Reserve Police Force), CISF (Central Industrial Security Force), ITBP (Indo-Tibetian Border Police), SSB (Sashastra Seema Bal), NSG (National Security Guard), SPG (Special Protection Group).
Each state Government’s administrative head of the Home Department of a state is an IAS officer who is also known as Additional Chief Secretary or Principal Secretary to the State government.
In each state, the DGP (Director General of Police) is considered as the head and is assisted by many DGPs or Special DGPs who look for a bureau within the state police (Law & Order, Crime, etc)
Some large states like Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, Tamil Nadu have divided the police force into Zones, Ranges and Commissionerates.
Commissioners are empowered with the powers of an executive magistrate and functions and are assisted by several joint commissioners of Police are incharge of a bureau (Law and Order, Crime, etc.), mirroring the organisation of the state police as a whole.
In smaller states like Andaman and Nicobar, Arunachal Pradesh, the police force is divided into different ranges only.
Further are the organisation outside commissionerate are as follows :-
•Zone police is headed by an IPS officer with the rank of IG or ADG.
•Range police is also headed by an IPS officer in the rank of IG or DIG.
•District police are headed by a Senior Superintendent or a Superintendent of Police.
•Area police are also headed by Superintendent of Police with a lower rank than district head.
•Sub Divisions are headed by DSP or ASP who are known as SDPO (sub divisional police officers). In some places, an inspector can also take charge of the circle.
•Police station is headed by an Inspector or Sub-inspector may be in charge of one police station. They are posted as Station House Officer and Station Officer respectively. They give commands to the other low ranking officers.
•Senior Constable (Hawaldar) who leads the team of constables and commands them.


