How does Sun fusion reaction works and can it be used to create electricity?
Sun generates both heat and light energy from a nuclear fusion (proton-proton fusion) process occurring inside its core. The Sun’s core consists of hydrogen molecules that are being converted into helium via nuclear fusion. The hydrogen atoms are fused into each helium atom and the mass is converted into energy. The innermost part of the Sun is its core which has 200 billion times greater atmospheric pressure than on Earth. In this high temperature and pressure, Hydrogen nuclei fuse together to form helium nuclei releasing energy in different forms. Energy is formed of small particles called neutrinos that have the ability to travel directly from Sun into the Solar System.
According to scientists, the fusion reaction takes place in the core of almost every star. In the fusion reaction, two light nuclei can merge to form a single nucleus. this process results in releasing energy because the total mass of the resulting nucleus is less than the mass of two original nuclei. The mass that is not being used after fusion has taken place results in forming energy according to Einstein’s equation of E=mc2. Reportedly the energy released from the fusion reaction can be used to generate clean energy.
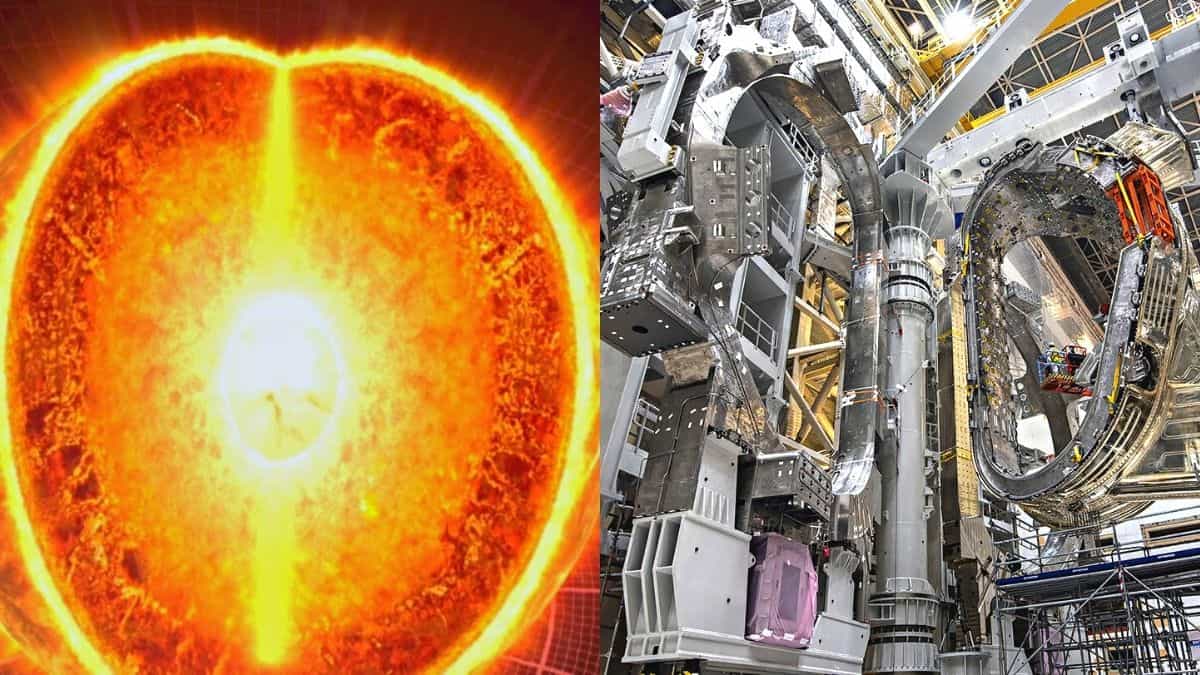
Scientists have developed a power plant the tokamak which is an experimental machine designed to use a powerful magnetic field to confine the plasma. The tokamak is designed to perform controlled thermodynamic fusion power, initially conceptualized by Soviet physicists Igor Tamm and Andrei Sakharov.
The concept of running the tokamak device is by producing energy via fusion reaction in its core. The energy produced can be absorbed as heat by the walls of the tokamak vessel. The absorbed heat is then used to produce steam and run turbines to generate electricity.
The tokamak device’s magnetic fields can contain and control hot plasma to perform fusion reactions. The device uses its different types of auxiliary heating methods to heat up the plasma particles. The fusion reaction usually takes place between deuterium and tritium (DT) nuclei that fuse to produce one helium nucleus, one neutron, and massive energy. The produced electrically charged helium nucleus then remains within the plasma due to the magnetic fields. The neutrally charged neutrons then carry away almost 80% of the energy from plasma and remain unaffected by the magnetic fields. The neutron’s kinetic energy is transferred into heat and gets absorbed by the surrounding walls of the tokamak.
The heat is then captured by cooling water circulating via the vessel’s walls in the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER). The steam is then dispersed through cooling towers. The steam can be used to run turbines in a process of generating electricity.
This is how the fusion reaction that is always occurring in the Sun’s core can be generated in a controlled artificial environment named ITER to generate electricity. Scientists are still in the process of experimenting to perform this as regular means of generating electricity.
However, according to the Xinhua News Agency, a group of scientists from China used the Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak or EAST to perform nuclear fusion and generated almost 158 million degrees Fahrenheit of temperature for only 1,056 seconds. Scientists claimed that this achievement has brought them closer to creating a source of nearly unlimited clean energy. EAST is expected to cost China $1 trillion by the time it finishes its experiment.
The International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) is currently being built in Marseille, France in collaboration with 35 countries including European Union, the U.K., China, India, and the U.S with a powerful magnetic field 280,000 times as strong as Earth. The reactor is expected to finish in 2025.


