Ross 508b, new super-Earth discovered 37 light years away, life support potentiality seems to exist
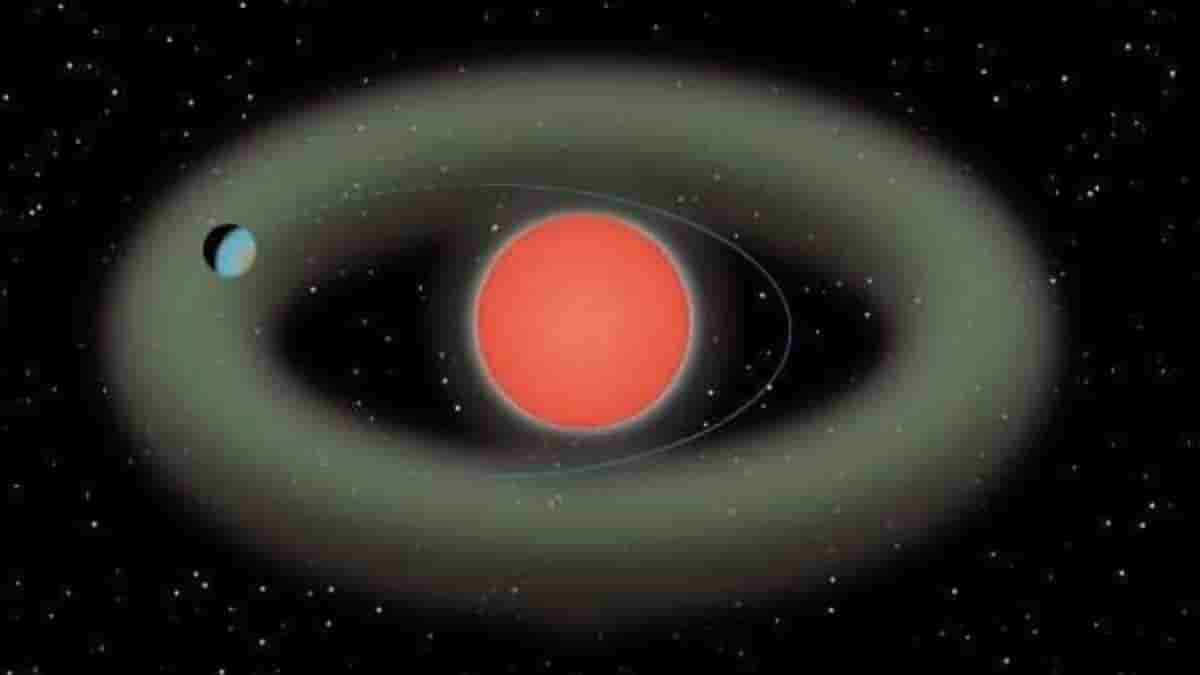
The Japan’s Subaru Telescope has recently discovered a super-Earth situated around the edges of the habitable zone of a red dwarf star. The distance of this super-Earth is 37 light-years from our planet.
The Subaru Strategic Programme was initiated in the year 2007, who’s goal was to produce outstanding scientific outcomes with the use of the Subaru Telescope. The super-Earth stands as it’s latest discovery.
This newly found super-Earth has been names as Ross 508b. Planet earth’s newly found sibling is a Rocky world with an estimated mass of four times that of planet Earth.
When it comes to the time correspondence, a year on Ross 508b lasts for just 11 Earth days. Thus we can derive that Ross 508b’s orbit is not that large. Additionally red dwarfs are much smaller compared to the Sun.
The smaller sizes leads to a narrow gravitational field. It’s not as expansive as the Sun’s. Ross 508b thus revolves at a distance of just 5 million kilometres from the red dwarf.
On comparing to Mercury, it can be derived that the planet is about 60 million kilometres from the Sun.
Ross 508b possesses an elliptical orbit, suggesting that it dips in and out of the habitable zone. The planet isn’t always too close to the dwarf star.
It is possible that such a planet may be able to retain water on its surface. Until then, existence of life and water on Ross 508b is up to the researchers to figure out.


